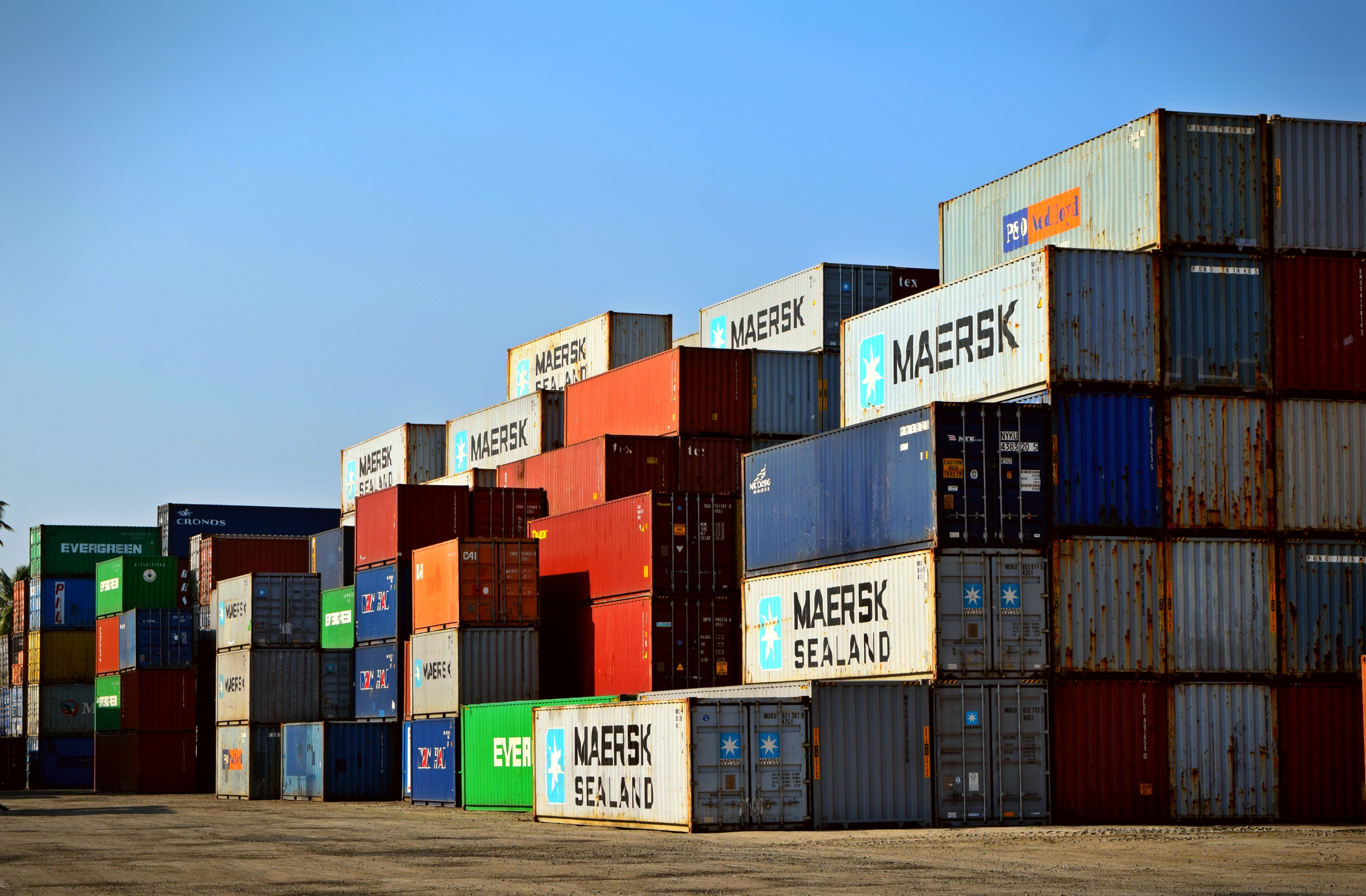
Container export operation process.
With the continuous growth of China's exports, the international freight industry has also developed considerably, especially in coastal port cities, the rapid development of international freight business has led to the growth of international freight employees year by year. Nowadays, professional freight forwarders have begun to develop to professional words and high efficiency. 1. Accept entrustment After receiving the entrustment from the cargo owner. It should be confirmed from the following aspects, including the filing (annual review) of the unit at the customs of the place of export; Whether the customs declaration documents are complete (the full set of customs declaration documents include the entrusted customs declaration agreement, export goods declaration form, packing list, invoice, contract, export foreign exchange verification form and various documents involved in customs supervision conditions); Whether the various documents required by the customs supervision conditions are complete; What kind of container the cargo is equipped with; Are there any special requirements, etc. 2. Booking According to the requirements of the cargo owner's shipping power of attorney, the packing point, port time and location of the space (obtaining the ship name, voyage, bill of lading) and the shipping company are determined. The shipping company or ship agent prepares the loading list and pre-provisioning list according to the booking and stowage reservation, and presets the ship map, cargo manifest, etc. to the terminal for receiving and loading. 3. Packing and collection port The freight forwarder picks up the container equipment handover slip from the shipping company or the shipping agent and picks up the empty container at the designated yard. After the freight forwarder packs the container at the storage location of the entrusted unit (or the entrusted unit delivers the goods to the freight forwarder's warehouse for packing), the container cargo is sent to the terminal together with the container packing list and equipment handover order. The terminal will send the loading list and container packing list provided by the shipping company or shipping agent to the customs for customs supervision and loading. 4. Customs declaration After receiving the goods, the dock will allocate the carrying capacity according to the pre-provisioned ship map and the pre-loaded list, and prepare the one-legged ship in the loading order. The first mate will pick up the load according to the loading list, and a station receipt will be issued after loading. After loading, the receipt of the terminal station shall be handed over by the terminal shipping company or the shipping agent. According to the actual situation of loading, the terminal draws the actual loading diagram and delivers it to the shipping company or shipping agent. The shipping company or shipping agent will deliver the actual ship chart, manifest, freight manifest, bill of lading, container packing list, etc. to the ship to the port of unloading. The box must enter the port to declare customs, and after the box is completed, it is submitted to the customs broker for customs declaration with the customs declaration information provided by the customer and the original matching receipt. After the customs verifies the shipment, it will stamp the loading list and release it, and return the loading list and station receipt to the freight forwarder. The freight forwarder will deliver the stamped loading list and station receipt to the dock distribution room. The terminal is cleared according to the receipt of the box entering the port and the customs declaration, and the ship is allocated. 5. Make a bill of lading Confirm the bill of lading with the customer 1-2 days before the ship departs. Make a bill of lading according to the relevant contents of the manifest and sea freight consignment, and fax the contents of the bill of lading to the principal to confirm that it is correct and make the official bill of lading. MB/L Shipping Company Bill of Lading (Sea Bill) HB/L Agency Bill There is an agent abroad, with this order, go to the agency to exchange the order. 6. Sending bills of lading and verifying tax refund documents After confirming that the goods have been loaded and departed, the full set of bills of lading should be sent to the principal as soon as possible so that they have sufficient time to complete the foreign exchange settlement procedures. The shipping company or shipping agent issues the bill of lading to the freight forwarder with the terminal receipt. The freight forwarder will send the loading bill of lading to the entrusted unit. The shipping company or shipping agent will send the manifest to customs. Customs checks invoices, tax refund forms and other documents to the freight forwarder according to the shipping manifest. The freight forwarder picks up the tax refund form, foreign exchange verification form, etc. and sends it to the entrusted unit.